Lijst met elementen
»
actinium
»
argon
»
astatine
»
barium
»
bismut
»
bohrium
»
Borium
»
broom
»
cadmium
»
calcium
»
cerium
»
cesium
»
chloor
»
chromium
»
curium
»
dubnium
»
erbium
»
europium
»
fermium
»
fluorine
»
fosfor
»
francium
»
gallium
»
goud
»
hafnium
»
hassium
»
helium
»
holmium
»
ijzer
»
indium
»
iridium
»
jodium
»
kalium
»
kobalt
»
koolstof
»
koperen
»
krypton
»
lantaan
»
lithium
»
Lood
»
lutecium
»
mangaan
»
natrium
»
neon
»
Nihonium
»
nikkel
»
niobium
»
nobelium
»
osmium
»
platina
»
polonium
»
radium
»
radon
»
rhenium
»
rhodium
»
rubidium
»
rutenium
»
samarium
»
scandium
»
selenium
»
silicium
»
stikstof
»
tallium
»
tantalum
»
Tennesse
»
terbium
»
thorium
»
thulium
»
tin
»
titanium
»
uranium
»
vanadium
»
wolfraam
»
xenon
»
yttrium
»
Zilver
»
zink
»
zuurstof
»
zwavel
mineralogie
elementen
C koolstof
C - koolstof - OVERIG NIET-METAAL
Koolstof is een chemisch element dat essentieel is voor het leven en voor de vervaardiging van allerlei soorten producten. Het wordt weergegeven door het symbool C en wordt in overvloed in het milieu aangetroffen als organische koolstof (zoals in steenkool, koolwaterstoffen, enz.) en in anorganische vorm (als kooldioxide [CO2], koolmonoxidekoolstof [CO], enz.). Het is een essentieel onderdeel van het georganiseerde leven op aarde.
koolstof is kleurloos, geurloos en combineert met andere elementen om organische en anorganische verbindingen te vormen. Het wordt beschouwd als een van de drie elementen die een grote rol spelen in de organische chemie (samen met waterstof en zuurstof). koolstof bindt zich met zichzelf en andere elementen om moleculen te vormen waarvan de eigenschappen worden bepaald door het type binding tussen de koolstofatomen.
koolstof is een veelzijdig element en de moleculen die het vormt kunnen verschillende eigenschappen hebben. De belangrijkste eigenschappen van koolstof zijn elektrische geleidbaarheid, thermische weerstand en het vermogen om vocht op te nemen. Producten gemaakt van koolstof worden veel gebruikt in de industrie en in het dagelijks leven. De belangrijkste op koolstof gebaseerde producten zijn brandstoffen, kunststoffen, kleurstoffen, inkten, staal, textiel en chemicaliën voor cosmetica en medicijnen.
koolstof is ook een belangrijk element voor de productie en opslag van energie. koolstof wordt gebruikt om energie op te wekken in elektriciteitscentrales en kan worden opgeslagen in de vorm van kolen, aardgas en olie. Fossiele brandstoffen kunnen worden omgezet in energie uit de koolstof die ze bevatten. koolstof kan ook worden opgeslagen in de vorm van biomassa (organisch plantaardig of dierlijk materiaal), kooldioxide of op koolstof gebaseerde chemicaliën.
koolstof is kleurloos, geurloos en combineert met andere elementen om organische en anorganische verbindingen te vormen. Het wordt beschouwd als een van de drie elementen die een grote rol spelen in de organische chemie (samen met waterstof en zuurstof). koolstof bindt zich met zichzelf en andere elementen om moleculen te vormen waarvan de eigenschappen worden bepaald door het type binding tussen de koolstofatomen.
koolstof is een veelzijdig element en de moleculen die het vormt kunnen verschillende eigenschappen hebben. De belangrijkste eigenschappen van koolstof zijn elektrische geleidbaarheid, thermische weerstand en het vermogen om vocht op te nemen. Producten gemaakt van koolstof worden veel gebruikt in de industrie en in het dagelijks leven. De belangrijkste op koolstof gebaseerde producten zijn brandstoffen, kunststoffen, kleurstoffen, inkten, staal, textiel en chemicaliën voor cosmetica en medicijnen.
koolstof is ook een belangrijk element voor de productie en opslag van energie. koolstof wordt gebruikt om energie op te wekken in elektriciteitscentrales en kan worden opgeslagen in de vorm van kolen, aardgas en olie. Fossiele brandstoffen kunnen worden omgezet in energie uit de koolstof die ze bevatten. koolstof kan ook worden opgeslagen in de vorm van biomassa (organisch plantaardig of dierlijk materiaal), kooldioxide of op koolstof gebaseerde chemicaliën.
Synthetisch
Radioactief
Vloeistof
Gasvormig
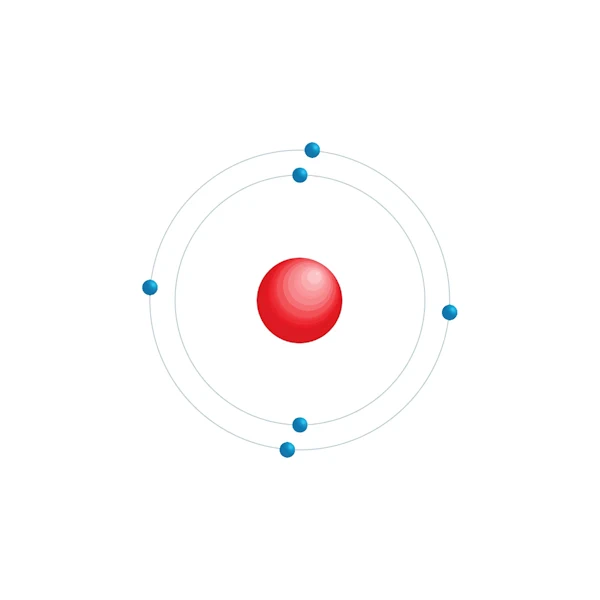
Elektronisch configuratiediagram
| Namn | koolstof |
| Aantal | 6 |
| Atomair | 12.0112 |
| Symbool | C |
| Fusie | 3550 |
| Koken | 4827 |
| Dichtheid | 2.267 |
| Periode | 2 |
| Groep | 14 |
| Ontdekking | 0 Prehistoric |
| Overvloed | 200 |
| Straal | 0.91 |
| Elektronegativiteit | 2.55 |
| Ionisatie | 11.2603 |
| Aantal isotopen | 7 |
| Elektronische configuratie | [He] 2s2 2p2 |
| Oxidatie stelt | -4,-3,-2,-1,1,2,3,4 |
| Elektron op energieniveau | 2,4 |
| Mineralen | Hardheid | Dichtheid |
| Abelsonite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.45 |
| Abenakiite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.21 |
| Acetamide | 1.00 / 1.50 | 1.17 |
| Adamsite-(Y) | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Aerinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Afghanite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.55 |
| Agaite | 6.99 | |
| Agricolaite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.53 |
| Albrechtschraufite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.60 |
| Alexkhomyakovite | ||
| Alloriite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.35 |
| Alstonite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.69 |
| Alumohydrocalcite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.23 |
| Amber | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.10 |
| Ammoniet | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.20 |
| Ancylite-(Ce) | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.90 |
| Ancylite-(La) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.88 |
| Andersonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.79 |
| Ankerite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.00 |
| Antipinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.55 |
| Aragoniet | 3.50 / 4.00 | 2.93 |
| Arisite-(Ce) | ||
| Arisite-(La) | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.07 |
| Armangite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.43 |
| Artinite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.00 |
| Ashburtonite | 4.69 | |
| Ashcroftine-(Y) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.61 |
| Astrocyanite-(Ce) | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.80 |
| Aurichalcite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.64 |
| Azuriet | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.77 |
| Balliranoite | ||
| Barbertonite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 2.10 |
| Barentsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.56 |
| Barringtonite | 2.83 | |
| Barstowite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.50 |
| Barytocalcite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.64 |
| Bastnäsite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.95 |
| Bastnäsite-(La) | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.95 |
| Bastnäsite-(Nd) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 5.23 |
| Bastnäsite-(Y) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.90 |
| Bayleyite | 2.05 | |
| Baylissite | 2.00 | |
| Benstonite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.60 |
| Beyerite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.56 |
| Bijvoetite-(Y) | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.90 |
| Biraite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.76 |
| Birunite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.36 |
| Bismutite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 7.00 |
| Blatonite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.99 |
| Bonshtedtite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.95 |
| Borcarite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.77 |
| Bosoite | ||
| Bradleyite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.73 |
| Braunerite | ||
| Brenkite | 3.10 | |
| Brianyoungite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 3.93 |
| Britvinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.51 |
| Brugnatellite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.14 |
| Burbankite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Burkeite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.57 |
| Bussenite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.63 |
| Bütschliite | 2.00 | |
| Calciet | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.71 |
| Calcioancylite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Calcioancylite-(Nd) | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Calcioburbankite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.45 |
| Calclacite | 1.00 | |
| Caledonite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 5.70 |
| Calkinsite-(Ce) | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.27 |
| Callaghanite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.71 |
| Camérolaite | 3.10 | |
| Canavesite | 1.80 | |
| Cancrinite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.40 |
| Cancrisilite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.40 |
| Caoxite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.85 |
| Carboborite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.12 |
| Carbobystrite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.37 |
| Carbocernaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.53 |
| Carbokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.14 |
| Carbonate-fluorapatite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.12 |
| Carbonate-hydroxylapatite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.00 |
| Carbonatecyanotrichite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.65 |
| Carborandiet | ||
| Caresite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.57 |
| Carletonite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.45 |
| Carpathite | 1.50 / 1.50 | 1.29 |
| Carraraite | ||
| Carrboydite | 2.50 | |
| Caysichite-(Y) | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.03 |
| Cebaite-(Ce) | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.81 |
| Cebaite-(Nd) | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.80 |
| Cejkaite | 3.67 | |
| Cerusite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.50 |
| Chalconatronite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.27 |
| Chanabayaite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.46 |
| Chaoite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 3.33 |
| Charmarite | ||
| Chibaite | 6.50 / 7.00 | 1.93 |
| Chlorartinite | 1.87 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se